Netty-4.1.20版本
1、线程模型
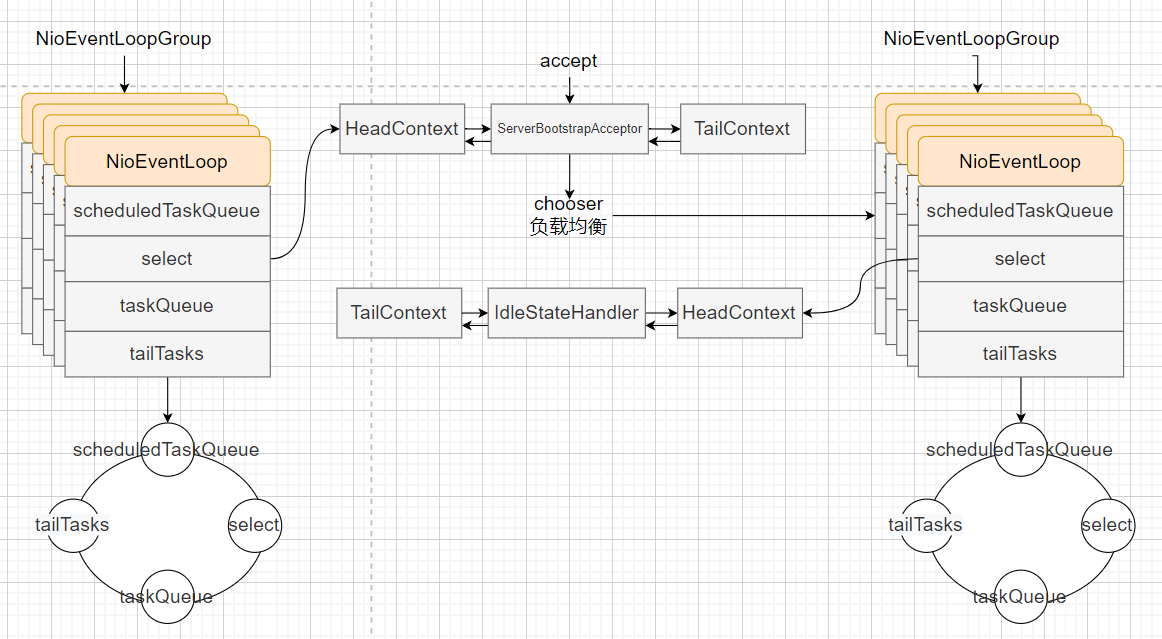
Netty中一般会创建两个事件循环组,一个为bossGroup,主要用于接收客户端连接,和处理三个队列任务。一个为workerGroup,主要用于处理客户端的读写事件,和三个队列中的任务。在workerGroup中,应该将耗时的业务逻辑放入新建的线程池中异步进行,让其尽可能的只处理select事件集。
在bossGroup中,每一个事件循环在开始时都会在selector中注册accept事件,当有accept事件发生时,会触发NioServerSocketChannel中的read方法,其中会调用责任链Pipeline中的fireChannelRead、fireChannelReadComplete事件,在ServerBootstarpAcceptor的channelRead方法中,会将传递的参数NioSocketchannel设置属性值并将其注册到workGroup其中一个EventLoop中,从此这个channel的所有事件都由此这一个事件循环负责,即单线程执行。
EventExecutorGroup、EventExecutor:事件执行组,主要是提交、执行任务。前者主要管理、调用后者。
EventLoopGroup、EventLoop:相较于EventExecutorGroup,增加了channel的注册功能。
2、启动流程
main
ServerBootstrap启动类,可以理解为门面模式,即简化内部实现细节。在调用其bind方法之前,都是对其内部属性的设置,方便启动时使用。这里就不过多解释,直接从bind方法开始看起。
xxxxxxxxxxstatic final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8009"));
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1); EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(); try { ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap(); //设置两个组 b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup) //这是bossGroup中的channel,workerGroup不用设置 .channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class) //设置bossGroup的责任链 .handler(new LoggingHandler(LogLevel.INFO)) //设置workerGroup的责任链 .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() { //当channel注册到select中后。会间接回调此函数 public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) { ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline(); //设置当前channel的责任链。心跳机制 p.addLast(new IdleStateHandler(12, 12, 0)); //添加HTTP解码器 p.addLast(new HttpServerCodec()); } });
ChannelFuture f = b.bind(PORT).sync(); f.channel().closeFuture().sync(); } finally { workerGroup.shutdownGracefully(); bossGroup.shutdownGracefully(); }}bind
主要作用:创建channel,设置accept感兴趣事件,并将其注册到selector中,注册完成后回调Pipeline的fireChannelRegistered、fireChannelActive
xxxxxxxxxxprivate ChannelFuture doBind(final SocketAddress localAddress) { //初始化channel,并注册到selector中 final ChannelFuture regFuture = initAndRegister(); final Channel channel = regFuture.channel(); if (regFuture.cause() != null) { return regFuture; } //如果已经注册完成 if (regFuture.isDone()) { ChannelPromise promise = channel.newPromise(); //开始绑定和监听 doBind0(regFuture, channel, localAddress, promise); return promise; } //未注册完成,添加观察者返回。}initAndRegister
创建channel,并初始化Pipeline等属性。之后将其注册到selector中。
xxxxxxxxxxfinal ChannelFuture initAndRegister() { Channel channel = null; try { channel = channelFactory.newChannel(); init(channel); } catch (Throwable t) { ... }
//其注册到selector中,注册完成后回调Pipeline的fireChannelRegistered、fireChannelActive ChannelFuture regFuture = config().group().register(channel); if (regFuture.cause() != null) { if (channel.isRegistered()) { channel.close(); } else { channel.unsafe().closeForcibly(); } } return regFuture;}init
设置channel中的属性,并往Pipeline中添加用户定义的handle,在下次循环中设置ServerBootstrapAcceptor,用于bossGroup将accept接受的连接发送到workerGroup中,完成workerGroup中注册。
xxxxxxxxxxvoid init(Channel channel) throws Exception { ... ChannelPipeline p = channel.pipeline(); p.addLast(new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() { public void initChannel(final Channel ch) throws Exception { final ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline(); ChannelHandler handler = config.handler(); if (handler != null) { pipeline.addLast(handler); }
ch.eventLoop().execute(new Runnable() { public void run() { pipeline.addLast(new ServerBootstrapAcceptor( ch, currentChildGroup, currentChildHandler, currentChildOptions, currentChildAttrs)); } }); } });}
3、Netty核心组件
事件循环组EventLoopGroup: 用于循环处理任务和连接请求
EventLoopGroup主要用于管理EventLoop,实际工作的是EventLoop
在创建EventLoopGroup时,在父类MultiThreadEventLoopGroup中会创建对应的EventLoop子类。并将其保存Chooser到集合中。
当execute时,会调用next方法负载均衡选个一个EventLoop执行任务。
对象池
Recycler: 将频繁使用销毁的对象缓存起来,减少频繁创建和销毁的性能损耗。Recycler,将对象保存到Stack中,使用栈充分利用先进后出,使得缓存行中的数据被充分利用。
主要使用FastThreadLocal,将对象池绑定到线程,当线程run方法完成之后,会调用removeAll移除所有。 当线程A创建对象将其传递给线程B,B释放时,会将对象放入其WeakOrderQueue的Link对象中,一个Link默认只保 存16个对象,多了之后会新建Link形成链表。
WeakOrderQueue用于管理Link。并且一个线程一个WeakOrderQueue,并且多个形成链表。在每次get获取时如果当前线程Stack中数量为空,则会在其他现成的WeakOrderQueue中转移一个Link的数量对象。
内存管理PoolArena: 为减少内外碎片,提高内存访问速度而设计。解决外碎片使用伙伴算法,解决内碎片使用Slab算法。
netty中:分为池化(PooledByteBufAllocator)和非池化内存(UnpooledByteBufAllocator)。
非池化:Java堆内存不存在内存泄漏、Java堆外内存存在内存泄漏
解决方案:DefaultResourceLeak类继承虚引用,关联buf对象。当buf引用被释放时:如果主动释放调用release 释放内存。则设置标志位free为false,否则检查ReferenceQueue里面的数据DefaultResourceLeak的标志位 free,如果为true表示未手动释放,则报内存泄漏。
责任链Pipeline: 使得对请求的处理高扩展、解耦合。
在每一个channel中绑定一个Pipeline,设置HeadContext(保证责任链从头开始处理,并且负责bind、write、flush等工作)和TailContext(保证责任链从尾部开始返回处理,并且释放资源等)。
业务自定义的handle会封装为DefaultChannelHandlerContext,加入到Pipeline链表中。
FastThreadLocal: 将index值在创建时就确定,不用每次都计算,增加性能。FastThreadLocal和ThreadLocal:
优势:
使用index,不用每次计算hash值
使用内存行对齐优化,避免内存行共享问题
劣势:
fastthreadLocal只有在线程run完成之后才会移除,会存在内存泄漏问题(netty内部使用没有问题)
index索引只会一直增加,即之前的位置不可以重复使用。
4、事件循环组
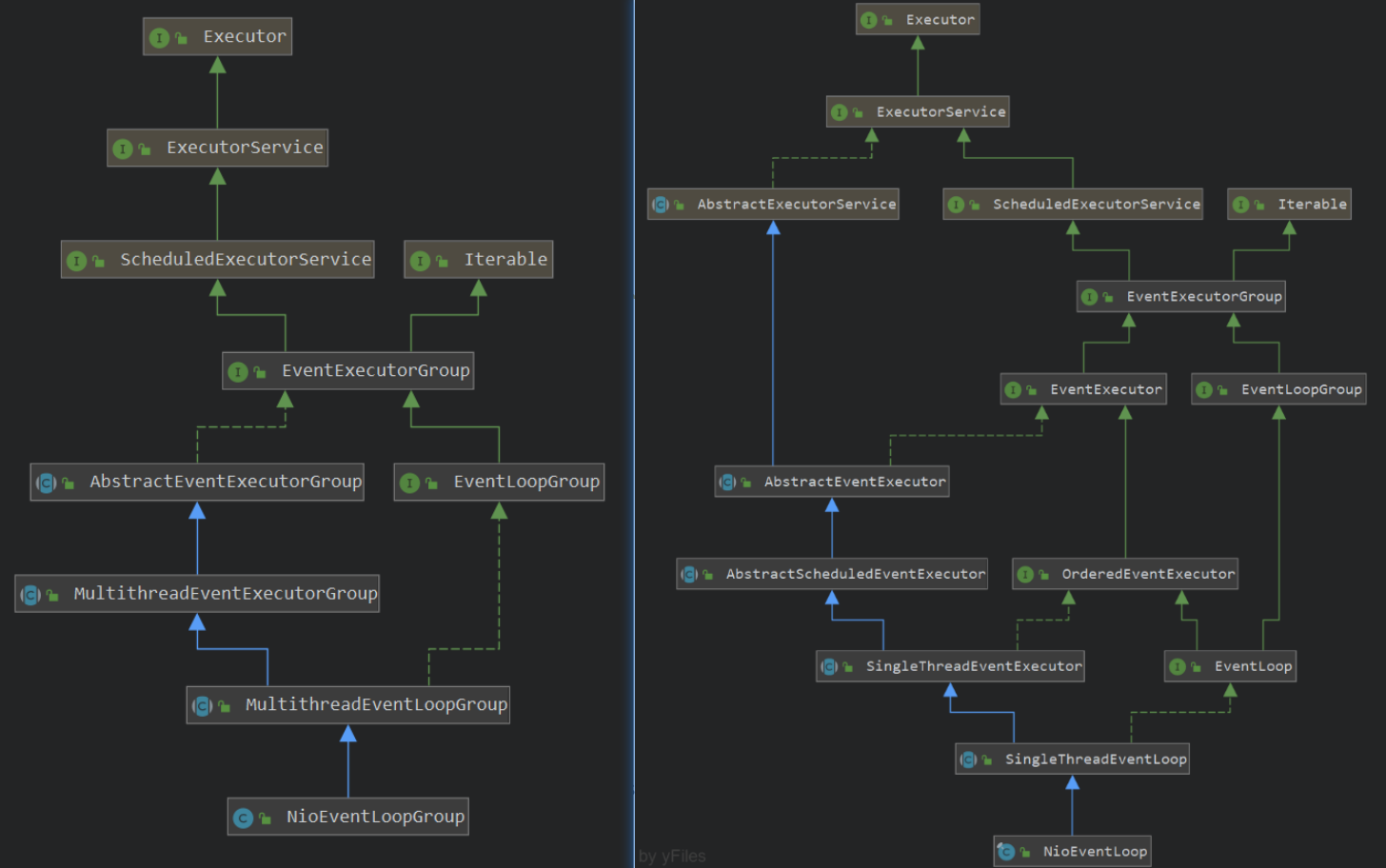
EventExecutorGroup接口:定义了事件执行器组属性,next()方法。AbstractEventExecutorGroup抽象类:默认实现,即方法全部交由next()执行。AbstractEventExecutor:组合了AbstractExecutorService和EventExecutor接口。AbstractScheduledEventExecutor:实现了延迟周期执行任务。MultithreadEventExecutorGroup模板类:事件执行器需要线程来执行,所以有了此类。通过Chooser实现了next()方法。在构造方法中,通过子类方法newChild()创建了
EventExecutor数组,即实际工作的事件执行器。SingleThreadEventExecutor:单线程执行器,定义taskQueue任务队列,并实现操作函数。MultithreadEventLoopGroup模板类:提供了channel的注册功能,所有方法交由next()执行。SingleThreadEventLoop:实际完成channel的注册功能。NioEventLoopGroup:实现了newChild()方法创建NioEventLoop对象。NioEventLoop:封装了nio操作。
NioEventLoop
根据策略选择有任务时阻塞还是执行select方法。之后根据执行比重分别执行io操作和处理task任务队列。所以在netty中的周期性任务是有很大延迟的,非必要不要往netty的taskQueue、tailTasks、scheduledTaskQueue三个队列中添加业务代码。
xxxxxxxxxxprotected void run() { for (;;) { try { //扩展点,创建时候自定义SelectStrategy switch (selectStrategy.calculateStrategy(selectNowSupplier, hasTasks())) { case SelectStrategy.CONTINUE: continue; case SelectStrategy.SELECT: select(wakenUp.getAndSet(false)); if (wakenUp.get()) { selector.wakeup(); } default: }
cancelledKeys = 0; needsToSelectAgain = false; final int ioRatio = this.ioRatio; //执行io和任务的比重 if (ioRatio == 100) { try { processSelectedKeys(); } finally { runAllTasks(); } } else { final long ioStartTime = System.nanoTime(); try { processSelectedKeys(); } finally { // Ensure we always run tasks. final long ioTime = System.nanoTime() - ioStartTime; runAllTasks(ioTime * (100 - ioRatio) / ioRatio); } } } catch (Throwable t) { handleLoopException(t); } }}processSelectedKey
处理io事件,通过select获取所有准备好的事件集,根据读写类型,分派执行。
xxxxxxxxxxprivate void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) { final AbstractNioChannel.NioUnsafe unsafe = ch.unsafe(); try { int readyOps = k.readyOps(); if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) { int ops = k.interestOps(); ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT; k.interestOps(ops); unsafe.finishConnect(); } //写事件 if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) { ch.unsafe().forceFlush(); } //读事件、accept事件 if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) { unsafe.read(); } } catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) { unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise()); }}runAllTasks
执行三个队列的任务。首先将周期队列中的已到期任务添加到taskQueue中,然后执行全部任务。之后在执行tailTasks任务。
xxxxxxxxxx// SingleThreadEventExecutor类 protected boolean runAllTasks() { boolean fetchedAll; boolean ranAtLeastOne = false; do { //将已到期的延迟队列任务添加到taskQueue中 fetchedAll = fetchFromScheduledTaskQueue(); //执行所有任务 if (runAllTasksFrom(taskQueue)) { ranAtLeastOne = true; } } while (!fetchedAll);
if (ranAtLeastOne) { lastExecutionTime = ScheduledFutureTask.nanoTime(); } //执行tailTasks任务 afterRunningAllTasks(); return ranAtLeastOne;}
5、内存管理
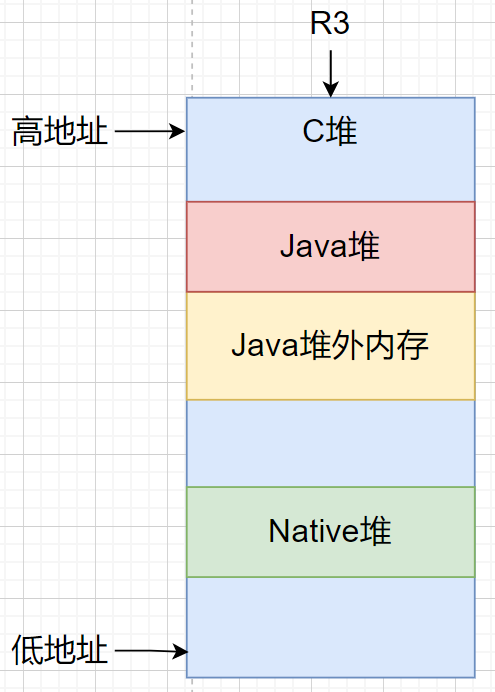
Java文件数据的复制过程
使用Java堆时:
读数据: 文件->内核堆->Native堆->Java堆
写数据:Java堆->Native堆->内核堆->文件
使用堆外内存时:
读数据: 文件->内核堆->Native堆->Java堆
Java堆外内存->内核堆->文件
使用mapp时:
读数据:文件->Java堆外内存->Java堆
写数据:Java堆外内存->文件
Java中的buffer
HeapByteBuffer:Java堆buffer,内存由JVM管理,自动垃圾回收。
DirectByteBuffer:直接使用C堆buffer,Java中直接操作address,而不需要将数据从Native堆复制到Java堆,但是JVM垃圾回收机制管理不到这些区域,需要手动释放。底层
malloc()、free()。MappedByteBuffer:文件内存映射。底层
mmap()、munmap()。
mmap内核实现原理
将在用户态进程的虚拟地址空间中创建一块和映射大小相同的区域vm_area_struct,将其插入到task_struct的mm_struct中,并且更新页表项pte。下次读取时根据虚拟地址,会检查pte。发生缺页异常,并将虚拟地址放入cr2寄存器中。在缺页异常处理中通过读取cr2中地址,将其转换为pte,根据属性进行不同映射。尝试在file的 address_space 结构的基数树中,查找所需的页面是否已经被缓存。如果页面已经缓存,则直接使用该页面;否则,需要从文件中读取数据并加载页面,并且更新页表项pte、tlb。
由于mmap会导致缺页异常、开始只分配虚拟内存。所有会存在两个问题:
缺页异常导致性能问题。可以使用预加载解决。即读取每一页的第一字节数据。很多框架都有使用。
只分配虚拟内存导致内存溢出。
JVM启动时会使用mmap分配Java堆内存。完成之后,当发生缺页异常时,正好此时Redis后台正在发生异步RDB或AOF重写,此时Redis会创建一个新的进程来后台执行。如果此时有大量数据被更改导致Redis占用的内存接近其原来的2倍(写时复制COW),占满了物理内存。而JVM缺页异常又需要分配新的物理内存,所有导致OOM。
Netty内存泄漏检测
Netty中内存分为:池化(PooledByteBufAllocator)和非池化(UnpooledByteBufAllocator)。
非池化:Java堆内存不存在内存泄漏(JVM垃圾回收)、Java堆外内存存在内存泄漏(虚引用,Cleaner类在buf引用被释放时,调用free释放堆外内存)虽然有Cleaner但是不及时,依靠JVM的GC,如果不GC就一直泄漏。
池化:都存在内存泄漏,即未主动调用release方法归还到内存池中。
解决内存泄漏:DefaultResourceLeak类继承虚引用(只需要跟踪对象而不需要Get,所以不适用弱引用),关联buf对象。当buf引用被释放时:如果主动释放调用release,则设置标志位free为false,否则检查ReferenceQueue里面的数据DefaultResourceLeak的标志位free,如果为true表示未手动释放,则报内存泄漏。
Netty内存池源码
总体架构图:
内存池前置知识:
内存池的作用是为了减少内、外碎片,增加内存分配性能。
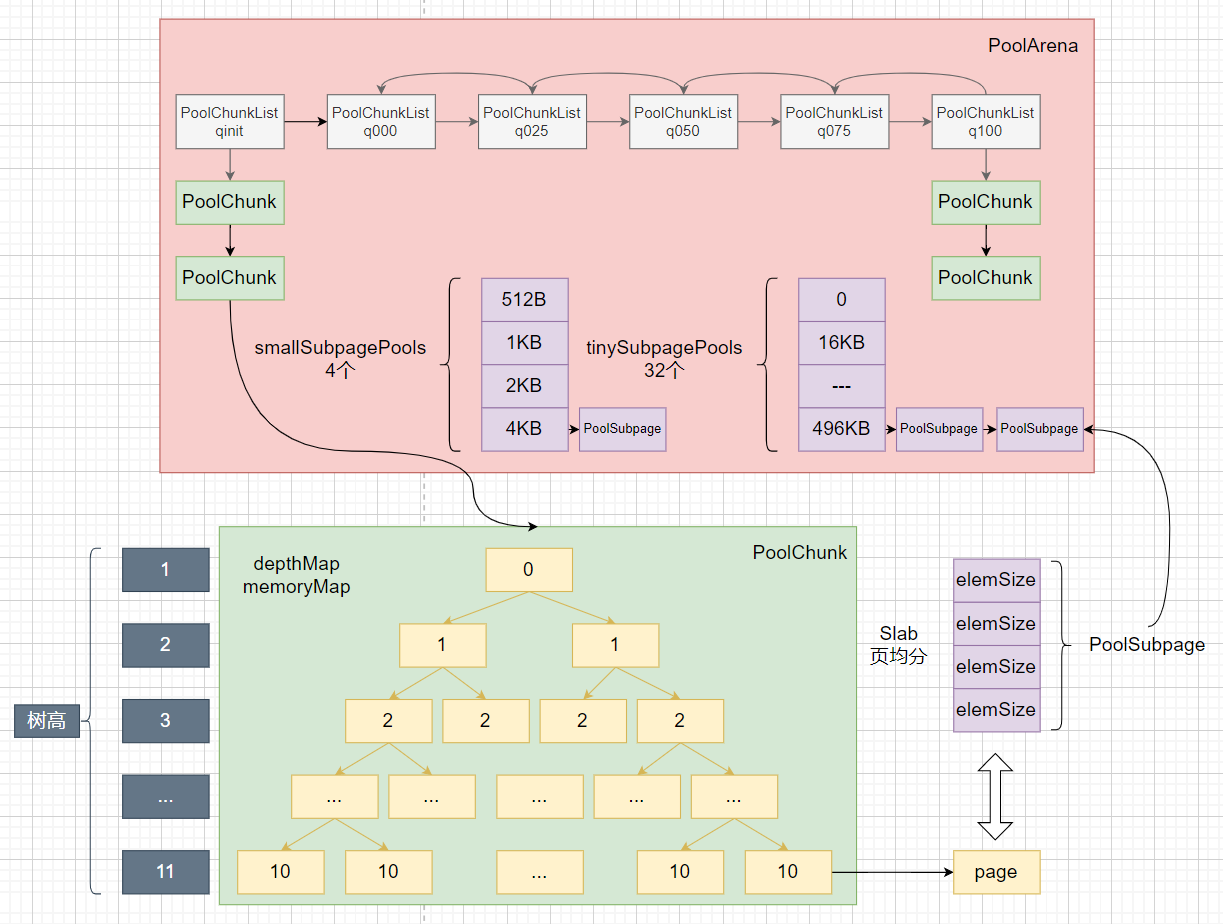
分为多个Arena内存区并且分为两种类型:heapArenas、directArenas。以减少线程竞争。在每个Arena中包含Chunk,默认大小为16Mb(伙伴算法使用完全二叉树,树节点也即一页最小为8Kb,树高11,所以一个Chunk大小为8192byte<<11=16Mb),当请求的内存小于一页时,使用Slab算法(将页均等分割),减少内碎片。那么一页按照多大分割呢?页类型分为两种小于512byte的
tinySubpagePools,大于512小于4Kb的smallSubpagePools。大于8Kb小于16Mb的normal。(由于对齐,所以4097byte也需要分配8Kb,此版本分配粒度还很大,内存浪费较高)tinySubpagePools:最小分割大小为16Byte,(大小公式:16*n)可分割类型为:0,16,32,48,...,496byte。一共32个挡位,即最大为496Byte。也即数组大小为32。根据大小求位置 X>>4。32>>4=2;(0位未使用)
smallSubpagePools:最小分割大小为512Byte,(大小公式:512*2^n)可分割类型为:512byte,1Kb,2Kb,4Kb。一共4个挡位,即最大为4Kb。也即数组大小为4。根据大小求位置 X>>10,看有多少个1即可。1Kb>>10=1;
normal:最小分割大小位8Kb,(大小公式:8Kb*n)可分配类型为:8Kb,16Kb,32Kb,...,16Mb。一共2048个挡位,即最大为16Mb。占满整个Chunk。
所以按照这36个挡位,将申请的内存对齐然后看属于哪一个,之后按照其大小将一页均分为等大小块。然后设置位图来表示这些块的使用情况。使用Long类型表示,因为一个Long可以表示64个位,而8Kb按照最小16Byte分割,也即被分为8*64份。所以最多需要8个Long即可表示全部块。之后将PoolSubpage添加到PoolArena的tinySubpagePools或smallSubpagePools数组中,用于下次快速从这个页中分配等大小内存。
PoolThreadCache线程缓存,以快速分配内存和减少竞争。当调用release时,根据Arena类型和内存大小,得到不同的Cache数组下标,将其封装为Entry添加到队列中。类似于PoolArena的tinySubpagePools或smallSubpagePools数组中,用于下次快速从当前线程的缓存中分配等大小内存。
伙伴算法,需要分配16KB内存如何查找?由于树节点为16MB,树高为0;二层为8MB,树高为1。以此类推。叶子节点为8KB,树高为11。所以只需要查找到树高为10的所有节点可不可用即可。根据大小capacity查询树高:depth = maxDepth - (log2(capacity) - pageShifts); depth = 11 - (log2(16 * 1024) - 13) = 11 - 1 = 10;
伙伴算法,如何计算当前树高能分配多大内存呢?根据树高depth 计算可分配内存大小:capacity = pageSize * 2 ^ (maxDepth - depth); 假设depth = 0,则capacity = 8KB * 2 ^ 11 = 16MB;假设depth = 10,则capacity = 8KB * 2 ^ 1 = 16KB;
使用:
xxxxxxxxxxByteBuf byteBuf = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.heapBuffer(4096);ByteBuf directBuffer = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(4096);CompositeByteBuf compositeByteBuf = PooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.compositeBuffer(4);
ByteBuf byteBuf1 = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.heapBuffer(4096);ByteBuf directBuffer1 = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.directBuffer(4096);CompositeByteBuf compositeByteBuf1 = UnpooledByteBufAllocator.DEFAULT.compositeBuffer(4);
directBuffer.release();源码:
PooledByteBufAllocator
创建HeapArena、DirectArena数组,实例化PoolArena。设置PoolThreadLocalCache类,用于线程本地缓存。当newXXBuffer时,通过threadCache.get()负载均衡获取一个HeapArena、DirectArena绑定到PoolThreadCache中。调用特定的Arena.allocate()方法分配内存ByteBuf。之后将其封装为LeakAwareByteBuf检测内存泄漏。
xxxxxxxxxx//nHeapArena、nDirectArena堆外内存、堆内存Arena个数通常为cpu核数//pageSize页大小 8KB//maxOrder最大数高 11public PooledByteBufAllocator(boolean preferDirect, int nHeapArena, int nDirectArena, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize, boolean useCacheForAllThreads, int directMemoryCacheAlignment) {
super(preferDirect); threadCache = new PoolThreadLocalCache(useCacheForAllThreads); //线程中保存的个数分别为512、256、64 this.tinyCacheSize = tinyCacheSize; this.smallCacheSize = smallCacheSize; this.normalCacheSize = normalCacheSize; chunkSize = validateAndCalculateChunkSize(pageSize, maxOrder); int pageShifts = validateAndCalculatePageShifts(pageSize); if (nHeapArena > 0) { heapArenas = newArenaArray(nHeapArena); List<PoolArenaMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolArenaMetric>(heapArenas.length); for (int i = 0; i < heapArenas.length; i ++) { PoolArena.HeapArena arena = new PoolArena.HeapArena(this, pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize, directMemoryCacheAlignment); heapArenas[i] = arena; metrics.add(arena); } //netty内存池指标检测 heapArenaMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics); } else { heapArenas = null; heapArenaMetrics = Collections.emptyList(); }
if (nDirectArena > 0) { directArenas = newArenaArray(nDirectArena); List<PoolArenaMetric> metrics = new ArrayList<PoolArenaMetric>(directArenas.length); for (int i = 0; i < directArenas.length; i ++) { PoolArena.DirectArena arena = new PoolArena.DirectArena(this, pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize, directMemoryCacheAlignment); directArenas[i] = arena; metrics.add(arena); } directArenaMetrics = Collections.unmodifiableList(metrics); } else { directArenas = null; directArenaMetrics = Collections.emptyList(); } metric = new PooledByteBufAllocatorMetric(this);}
protected ByteBuf newHeapBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) { PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get(); PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = cache.heapArena;
final ByteBuf buf; if (heapArena != null) { buf = heapArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } else { //直接分配非洲池化内存 buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ? new UnpooledUnsafeHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) : new UnpooledHeapByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } //内存泄漏检测 return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);}
protected ByteBuf newDirectBuffer(int initialCapacity, int maxCapacity) { PoolThreadCache cache = threadCache.get(); PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena = cache.directArena;
final ByteBuf buf; if (directArena != null) { buf = directArena.allocate(cache, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } else { //直接分配非洲池化内存 buf = PlatformDependent.hasUnsafe() ? UnsafeByteBufUtil.newUnsafeDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity) : new UnpooledDirectByteBuf(this, initialCapacity, maxCapacity); } //内存泄漏检测 return toLeakAwareBuffer(buf);}PoolArena
创建tiny、small子页集合tinySubpagePools、smallSubpagePools。并创建PoolChunkList集合链表。表示不同的内存使用率的Chunk。
分配内存:
内存对齐2^n,方便位运算。
小于一页8KB
小于512B,首先线程缓存分配,获取tinySubpagePools数组下标项PoolSubpage。
大于等于512B,首先线程缓存分配,获取smallSubpagePools数组下标项PoolSubpage。
如果PoolSubpage为空,表示没有可用子页。
5个PoolChunkList中分配。都为空时,创建新的PoolChunk,调用allocate。
否则直接在已有的PoolSubpage中分配,调用allocate。
小于等于16MB
首先线程缓存分配。
5个PoolChunkList中分配。都为空时,创建新的PoolChunk,调用allocate。
大于16MB
创建非池化内存。
handle:
小于一页时,伙伴算法中的叶子节点索引和一页均分数组下标
大于一页时,伙伴算法中的叶子节点索引
xxxxxxxxxxabstract class PoolArena<T> implements PoolArenaMetric { static final int numTinySubpagePools = 512 >>> 4;
private final PoolSubpage<T>[] tinySubpagePools; private final PoolSubpage<T>[] smallSubpagePools;
private final PoolChunkList<T> q050; private final PoolChunkList<T> q025; private final PoolChunkList<T> q000; private final PoolChunkList<T> qInit; private final PoolChunkList<T> q075; private final PoolChunkList<T> q100;
protected PoolArena(PooledByteBufAllocator parent, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int cacheAlignment) { this.parent = parent; this.pageSize = pageSize; this.maxOrder = maxOrder; this.pageShifts = pageShifts; this.chunkSize = chunkSize; directMemoryCacheAlignment = cacheAlignment; directMemoryCacheAlignmentMask = cacheAlignment - 1; //高位置1 capacity & subpageOverflowMask == 0小于pageSize subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1); tinySubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numTinySubpagePools); for (int i = 0; i < tinySubpagePools.length; i ++) { tinySubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize); } //pageShifts页大小偏移 1<<pageShifts==8192 numSmallSubpagePools = pageShifts - 9; smallSubpagePools = newSubpagePoolArray(numSmallSubpagePools); for (int i = 0; i < smallSubpagePools.length; i ++) { smallSubpagePools[i] = newSubpagePoolHead(pageSize); }
q100 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, null, 100, Integer.MAX_VALUE, chunkSize); q075 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q100, 75, 100, chunkSize); q050 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q075, 50, 100, chunkSize); q025 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q050, 25, 75, chunkSize); q000 = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q025, 1, 50, chunkSize); qInit = new PoolChunkList<T>(this, q000, Integer.MIN_VALUE, 25, chunkSize);
//设置前区节点 q100.prevList(q075); q075.prevList(q050); q050.prevList(q025); q025.prevList(q000); q000.prevList(null); qInit.prevList(qInit); }
PooledByteBuf<T> allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, int reqCapacity, int maxCapacity) { PooledByteBuf<T> buf = newByteBuf(maxCapacity); //设置buf的属性,用于回收到内存池中 allocate(cache, buf, reqCapacity); return buf; }
private void allocate(PoolThreadCache cache, PooledByteBuf<T> buf, final int reqCapacity) { //内存对齐 2^n次方 final int normCapacity = normalizeCapacity(reqCapacity); // capacity < pageSize 小于8KB if (isTinyOrSmall(normCapacity)) { int tableIdx; PoolSubpage<T>[] table; //位运算判断大小 boolean tiny = isTiny(normCapacity); if (tiny) { // < 512byte //线程缓存中分配 if (cache.allocateTiny(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { return; } //通过大小,在tinySubpagePools中找到下标,前置知识2 tableIdx = tinyIdx(normCapacity); table = tinySubpagePools; } else { //线程缓存中分配 if (cache.allocateSmall(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { return; } //通过大小,在smallSubpagePools中找到下标,前置知识3 tableIdx = smallIdx(normCapacity); table = smallSubpagePools; } //找到同大小的PoolSubpage链表 final PoolSubpage<T> head = table[tableIdx]; synchronized (head) { final PoolSubpage<T> s = head.next; //缓存为空,没有可用的Chunk if (s != head) { long handle = s.allocate(); s.chunk.initBufWithSubpage(buf, handle, reqCapacity); return; } } synchronized (this) { allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity); } return; } //大于一页8KB小于16MB if (normCapacity <= chunkSize) { //线程缓存中分配 if (cache.allocateNormal(this, buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { return; } synchronized (this) { allocateNormal(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity); } } else { //大于16MB直接分配非池化内存 allocateHuge(buf, reqCapacity); } }
private void allocateNormal(PooledByteBuf<T> buf, int reqCapacity, int normCapacity) { if (q050.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q025.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q000.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || qInit.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity) || q075.allocate(buf, reqCapacity, normCapacity)) { return; }
PoolChunk<T> c = newChunk(pageSize, maxOrder, pageShifts, chunkSize); long handle = c.allocate(normCapacity); c.initBuf(buf, handle, reqCapacity); qInit.add(c); }}PoolChunk
管理伙伴算法,初始化完全二叉树,并且初始化所有的叶子节点的集合。
xxxxxxxxxxfinal class PoolChunk<T> implements PoolChunkMetric { //保存所有叶子节点2048个 private final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages; final PoolArena<T> arena; //保存完全二叉树的节点使用情况 private final byte[] memoryMap; //初始值用于恢复 private final byte[] depthMap; //使用标记,伙伴算法,节点值等于当前层数。如果大于最大层,表示已使用 private final byte unusable; //剩余容量,用于计算使用比 private int freeBytes; PoolChunkList<T> parent; PoolChunk<T> prev; PoolChunk<T> next;
PoolChunk(PoolArena<T> arena, T memory, int pageSize, int maxOrder, int pageShifts, int chunkSize, int offset) { unpooled = false; this.arena = arena; this.memory = memory; this.pageSize = pageSize; this.pageShifts = pageShifts; this.maxOrder = maxOrder; this.chunkSize = chunkSize; this.offset = offset; unusable = (byte) (maxOrder + 1); log2ChunkSize = log2(chunkSize); subpageOverflowMask = ~(pageSize - 1); freeBytes = chunkSize; maxSubpageAllocs = 1 << maxOrder; //用于检测伙伴算法节点是否已分配 memoryMap = new byte[maxSubpageAllocs << 1]; //用于重新设置memoryMap depthMap = new byte[memoryMap.length]; int memoryMapIndex = 1; //设置每层的所有节点值为当前树高depth-1 for (int d = 0; d <= maxOrder; ++ d) { int depth = 1 << d; //树每一层节点数,2^n for (int p = 0; p < depth; ++ p) { memoryMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d; depthMap[memoryMapIndex] = (byte) d; memoryMapIndex ++; } } //子夜数组2948个 subpages = newSubpageArray(maxSubpageAllocs); }
//分配大于等于一页的内存 private long allocateRun(int normCapacity) { //计算出normCapacity所在的树高,前置知识7 int d = maxOrder - (log2(normCapacity) - pageShifts); //计算伙伴算法分配的节点索引 int id = allocateNode(d); if (id < 0) { return id; } freeBytes -= runLength(id); return id; }
//分配小于一页的内存 private long allocateSubpage(int normCapacity) { PoolSubpage<T> head = arena.findSubpagePoolHead(normCapacity); synchronized (head) { int d = maxOrder; //计算伙伴算法分配的节点索引 int id = allocateNode(d); if (id < 0) { return id; } //所有叶子节点集合 final PoolSubpage<T>[] subpages = this.subpages; final int pageSize = this.pageSize; //更新使用率 freeBytes -= pageSize; //算出是第几个叶子 int subpageIdx = subpageIdx(id); PoolSubpage<T> subpage = subpages[subpageIdx]; if (subpage == null) { subpage = new PoolSubpage<T>(head, this, id, runOffset(id), pageSize, normCapacity); subpages[subpageIdx] = subpage; } else { subpage.init(head, normCapacity); } return subpage.allocate(); } }
//d=10,1 << d = 1024;也即最多查询到1024节点处 private int allocateNode(int d) { int id = 1; //高位置1,当树深的第一个节点下标 int initial = - (1 << d); //树根节点的分配树高值 byte val = value(id); if (val > d) { return -1; } //保证val==d,树高小于d,继续向下查找。如下图id=4时所示 while (val < d || (id & initial) == 0) { id <<= 1; val = value(id); if (val > d) { id ^= 1; val = value(id); } } //标记为12,树高+1 setValue(id, unusable); //更新父节点的值,为子节点最小值 updateParentsAlloc(id); return id; }}allocateNode方法
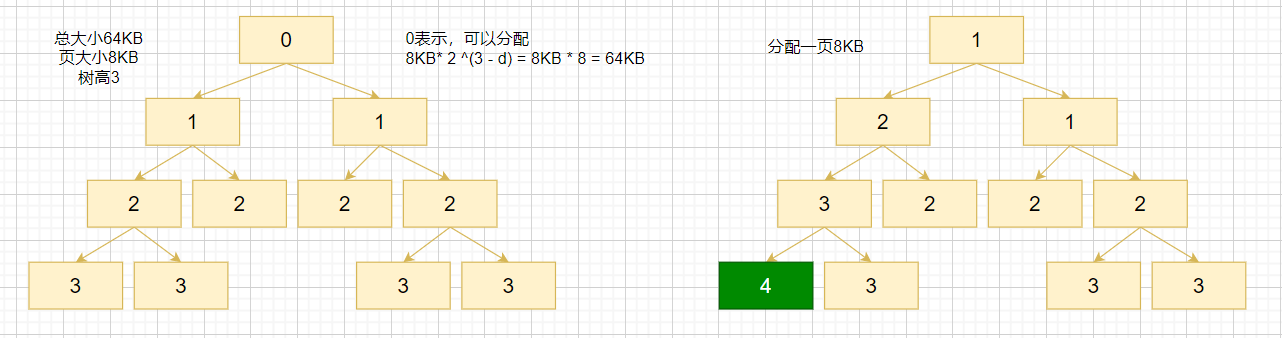
假设:d = 3,initial = 0111 1111 1000,如图
| id | val | 操作 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | (val < d || (id & initial) == 0)= true |
| 2 | 2 | (val < d || (id & initial) == 0)= true |
| 4(0100) | 3 | val == d 但是(val < d ||(id & initial) == 0)= true |
| 8 | 4 | for循环中:val > d,id ^= 1 |
| 9(1001) | 3 | (val < d || (id & initial) == 0)= false |
PoolSubpage
创建分割大小,并创建相应的位图表示使用情况。allocate时,找到一个未使用的位,标记即可。
xxxxxxxxxx
final class PoolSubpage<T> implements PoolSubpageMetric { final PoolChunk<T> chunk; //在伙伴算法中的节点索引 private final int memoryMapIdx; private final int runOffset; //8KB 8192Byte 最小分割为16Byte。所以有512个,那么就需要512位来表示使用情况。 private final int pageSize; //8个 使用long型,一个可以表示64个,那么一共需要512/64 = 8个 private final long[] bitmap; PoolSubpage<T> prev; PoolSubpage<T> next; //实际分割大小 int elemSize; //需要使用的位图位数 private int maxNumElems; //bitmap数组个数 private int bitmapLength; //下一个没使用的位图位置 最大值:111 111111,前3位表示是在哪一个bitmap, 后6位表示在哪个位 private int nextAvail; //当前有效数 private int numAvail; PoolSubpage(int pageSize) { chunk = null; memoryMapIdx = -1; runOffset = -1; elemSize = -1; this.pageSize = pageSize; bitmap = null; }
PoolSubpage(PoolSubpage<T> head, PoolChunk<T> chunk, int memoryMapIdx, int runOffset, int pageSize, int elemSize) { this.chunk = chunk; this.memoryMapIdx = memoryMapIdx; this.runOffset = runOffset; this.pageSize = pageSize; // pageSize / 16 / 64 bitmap = new long[pageSize >>> 10]; init(head, elemSize); } //elemSize = 1024为例 void init(PoolSubpage<T> head, int elemSize) { doNotDestroy = true; this.elemSize = elemSize; if (elemSize != 0) { // 8位即可表示 maxNumElems = numAvail = pageSize / elemSize; nextAvail = 0; //算出需要几个long 也即几个64位 bitmapLength = maxNumElems >>> 6; //不足1按照1计算。也即1个就可以。 if ((maxNumElems & 63) != 0) { bitmapLength ++; } for (int i = 0; i < bitmapLength; i ++) { bitmap[i] = 0; } } //添加到Arena的XXSubpagePools中 addToPool(head); } long allocate() { //获取未使用的位图索引 final int bitmapIdx = getNextAvail(); //8个long中第几个 int q = bitmapIdx >>> 6; //64位中哪一位 int r = bitmapIdx & 63; //设置标志位 bitmap[q] |= 1L << r; //如果都被使用,则从pool中移除 if (-- numAvail == 0) { removeFromPool(); } return toHandle(bitmapIdx); }}PoolThreadLocalCache
负载均衡从数组中获取heapArena、heapArena,并创建PoolThreadCache。
xxxxxxxxxxprotected synchronized PoolThreadCache initialValue() { final PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena = leastUsedArena(heapArenas); final PoolArena<ByteBuffer> heapArena = leastUsedArena(directArenas);
Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); if (useCacheForAllThreads || current instanceof FastThreadLocalThread) { return new PoolThreadCache( heapArena, directArena, tinyCacheSize, smallCacheSize, normalCacheSize, DEFAULT_MAX_CACHED_BUFFER_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_CACHE_TRIM_INTERVAL); } return new PoolThreadCache(heapArena, directArena, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);}PoolThreadCache
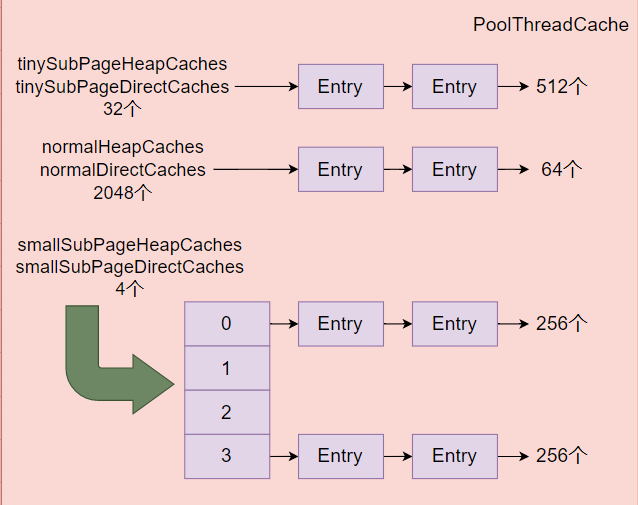
保存6种不同类型长度的集合:tinySubPageXXXCaches、smallSubPageXXXCaches、normalXXXCaches。当调用release释放池化内存时,会将其添加到对应大小的XXXCaches中的中queue链表中,下次该线程申请等大小内存时,就会直接从线程缓存中分配。
xxxxxxxxxx PoolThreadCache(PoolArena<byte[]> heapArena, PoolArena<ByteBuffer> directArena, int tinyCacheSize, int smallCacheSize, int normalCacheSize, int maxCachedBufferCapacity, int freeSweepAllocationThreshold) { this.freeSweepAllocationThreshold = freeSweepAllocationThreshold; this.heapArena = heapArena; this.directArena = directArena; if (directArena != null) { tinySubPageDirectCaches = createSubPageCaches(tinyCacheSize, PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools, SizeClass.Tiny); tinySubPageDirectCaches = createSubPageCaches(smallCacheSize, directArena.numSmallSubpagePools, SizeClass.Small); numShiftsNormalDirect = log2(directArena.pageSize); normalDirectCaches = createNormalCaches(normalCacheSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity, directArena); directArena.numThreadCaches.getAndIncrement(); } else { tinySubPageDirectCaches = null; smallSubPageDirectCaches = null; normalDirectCaches = null; numShiftsNormalDirect = -1; } if (heapArena != null) { tinySubPageHeapCaches = createSubPageCaches(tinyCacheSize, PoolArena.numTinySubpagePools, SizeClass.Tiny); smallSubPqiageHeapCaches = createSubPageCaches(smallCacheSize, heapArena.numSmallSubpagePools, SizeClass.Small); numShiftsNormalHeap = log2(heapArena.pageSize); normalHeapCaches = createNormalCaches(normalCacheSize, maxCachedBufferCapacity, heapArena); heapArena.numThreadCaches.getAndIncrement(); } else { tinySubPageHeapCaches = null; smallSubPageHeapCaches = null; normalHeapCaches = null; numShiftsNormalHeap = -1; } }freeSweepAllocationThreshold
当线程保存的本地对象太多时,会占用无用的内存空间。所以当线程allocate分配次数达到一定阈值时,会调用trim方法释放6个数组中不常用的缓存对象。何为不常用,以smallSubPqiageHeapCaches为例,其链表长度queue为256。如果分配次数为2。则表示最多有两个常用的也即最多只需要保存两个对象其余全部释放,如果当前Chunk使用率小于其最小值则移动到下一个PoolChunkList中,如果使用率等于0,则destroyChunk,heap类型的不用处理,因为已经没有强引用指向Chunk了,GC会自动回收。对于direct类型的需要调用freeMemory或者Cleaner类的clean方法。
6、责任链
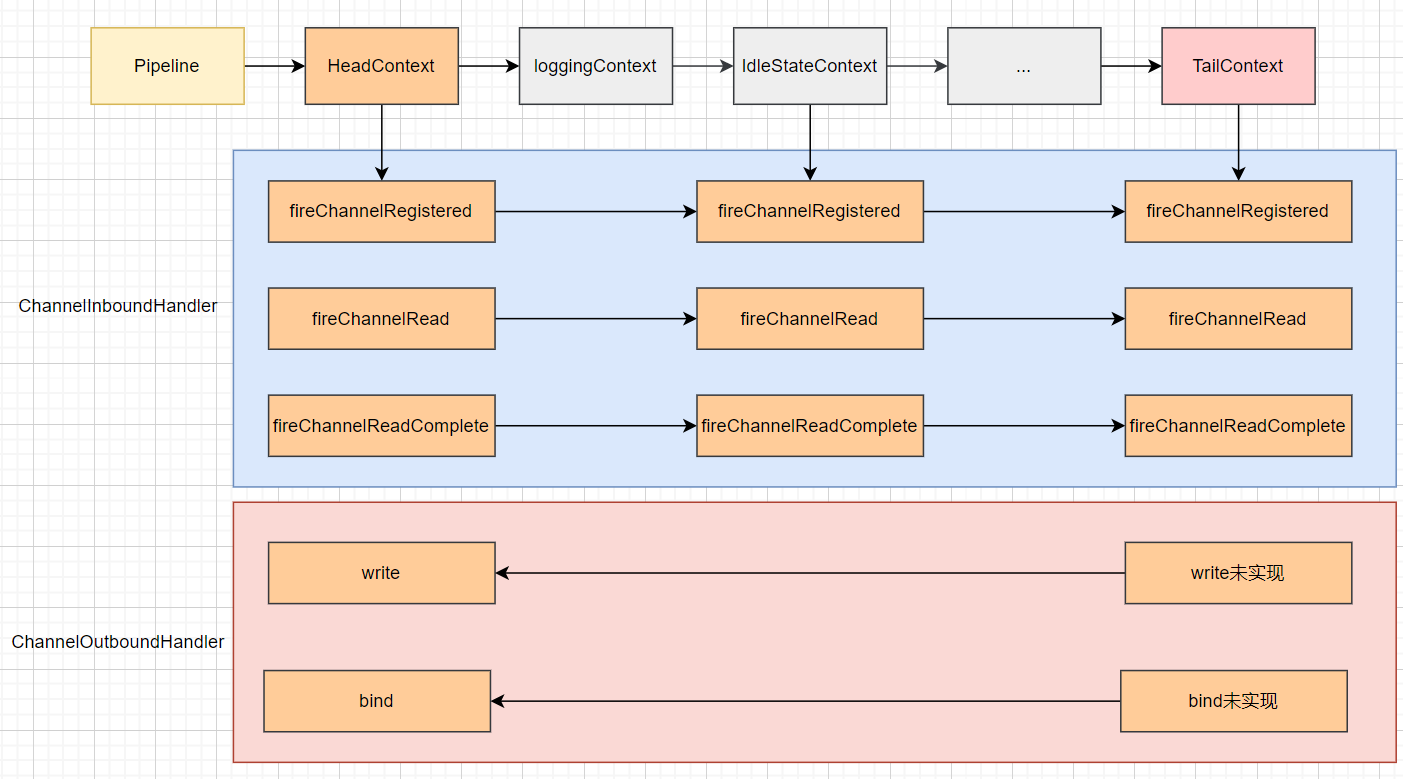
ChannelInboundInvoker、ChannelOutboundInvoker定义了各种事件通知函数fireChannelRead...
ChannelInboundHandler、ChannelOutboundHandler定义了各种事件通知函数的实现函数channelRead...
ChannelHandlerContext
xxxxxxxxxxpublic interface ChannelHandlerContext extends ChannelInboundInvoker, ChannelOutboundInvoker {
Channel channel();
EventExecutor executor();
String name();
ChannelHandler handler();
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRegistered();
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelUnregistered();
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelActive();
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelInactive();
ChannelHandlerContext fireExceptionCaught(Throwable cause);
ChannelHandlerContext fireUserEventTriggered(Object evt);
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRead(Object msg);
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelReadComplete();
ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelWritabilityChanged();
ChannelHandlerContext read();
ChannelHandlerContext flush();
ChannelPipeline pipeline();
ByteBufAllocator alloc();}AbstractChannelHandlerContext
实现了各种事件方法。fireChannelRegistered事件发生时,调用下一个继续执行ChannelRegistered。其他事件同样地道理。它只负责调用下一个,而自己的实现方法是由上一个调用的。
xxxxxxxxxxabstract class AbstractChannelHandlerContext implements ChannelHandlerContext { volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext next; volatile AbstractChannelHandlerContext prev; private final boolean inbound; private final boolean outbound; final EventExecutor executor; AbstractChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name,boolean inbound, boolean outbound) { this.pipeline = pipeline; this.executor = executor; this.inbound = inbound; this.outbound = outbound; }
public ChannelHandlerContext fireChannelRegistered() { invokeChannelRegistered(findContextInbound()); return this; }
static void invokeChannelRegistered(final AbstractChannelHandlerContext next) { EventExecutor executor = next.executor(); if (executor.inEventLoop()) { next.invokeChannelRegistered(); } else { executor.execute(new Runnable() { public void run() { next.invokeChannelRegistered(); } }); } }
private void invokeChannelRegistered() { if (invokeHandler()) { try { ((ChannelInboundHandler) handler()).channelRegistered(this); } catch (Throwable t) { notifyHandlerException(t); } } else { fireChannelRegistered(); } }}DefaultChannelHandlerContext
这个类,是所有用户自定义Hander的包装类。在调用channel.pipeline().addLast()时都会将handler封装为DefaultChannelHandlerContext。保存当前责任链和执行环境。
xxxxxxxxxxfinal class DefaultChannelHandlerContext extends AbstractChannelHandlerContext {
private final ChannelHandler handler;
DefaultChannelHandlerContext(DefaultChannelPipeline pipeline, EventExecutor executor, String name, ChannelHandler handler) { super(pipeline, executor, name, isInbound(handler), isOutbound(handler)); this.handler = handler; }
public ChannelHandler handler() { return handler; }
private static boolean isInbound(ChannelHandler handler) { return handler instanceof ChannelInboundHandler; }
private static boolean isOutbound(ChannelHandler handler) { return handler instanceof ChannelOutboundHandler; }}DefaultChannelPipeline
当channel的读写等事件发生时,会调用其绑定的Pipeline的相应方法:fireChannelRead、fireChannelRegistered。
而每个Pipeline中第一个Context是HeadContext、最后一个Context是TailContext。而HeadContext的fireXXX都是调用下一个执行。
xxxxxxxxxxpublic class DefaultChannelPipeline implements ChannelPipeline { final AbstractChannelHandlerContext head; final AbstractChannelHandlerContext tail;
protected DefaultChannelPipeline(Channel channel) { this.channel = ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(channel, "channel"); succeededFuture = new SucceededChannelFuture(channel, null); voidPromise = new VoidChannelPromise(channel, true);
tail = new TailContext(this); head = new HeadContext(this);
head.next = tail; tail.prev = head; }
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelRegistered() { AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRegistered(head); return this; }
public final ChannelPipeline fireChannelRead(Object msg) { AbstractChannelHandlerContext.invokeChannelRead(head, msg); return this; }}